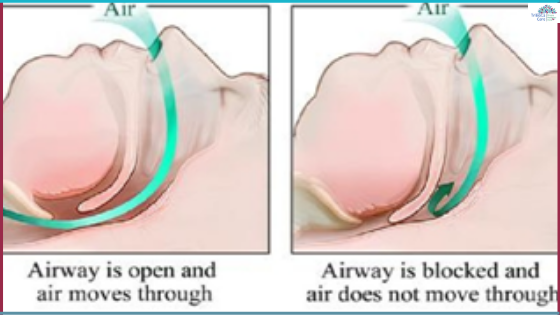
Obstructive sleep apnea (OSA) is a very common category of sleep apnea. It is a sleeping disorder, where an obstruction in the upper respiratory tract causes a temporary suspension of breathing. Apneas are characterized by a sudden loss of oxygen supply while we are asleep, and might even have fatal consequences if they are left untreated.
Sleep apnea, in general adversely affects our daily functionality by interfering with our sleep cycle, and increases the chances of having poor cardiovascular health.
What causes Obstructive Sleep Apnea?
While sleeping, the throat muscle relaxes excessively in people suffering from Obstructive sleep apnea. This results in the constriction of the air passage, causing difficulty in breathing.
Sleep apnea reduces the oxygen level in your bloodstream. The brain senses this disorder and sends a signal to the body and abruptly wakes it up so that the respiratory process can be normalized.
Several physical factors can cause Obstructive sleep apnea.
Bodyweight
It has been observed that people who are overweight are more prone to sleep apnea. Fat deposition in the upper respiratory tract can cause hindrance in breathing.
High blood pressure
Research shows that people with high blood pressure (hypertension) are more susceptible to the disorder.
Narrow respiratory tract
People with congenital respiratory tract disorder, such as narrow airway are at more risk than normal people.
Lifestyle
Smoking and consumption of alcohol increase the chance of developing Obstructive Sleep Apnea.
Symptoms
Most people suffering from sleep apnea are unaware of it. However, it might manifest in a number of symptoms like
- Snoring during sleep.
- Lethargy and daytime sleepiness.
- Poor cognitive function and inability to concentrate.
- Episodes of stopped breathing while sleeping, followed by gasping and abruptly waking up.
How does Sleep Apnea affect your cardiovascular health?
Research has shown that people with cardiovascular disorders such as hypertension are more at risk from obstructive sleep apnea.
However, people with no history of cardiovascular disorder might be at risk of developing complications if they are suffering from sleep apnea. A sudden obstruction in the respiratory passage causes the oxygen levels in your bloodstream to drop suddenly. It may increase the blood pressure, and puts a strain on the cardiovascular system.
Increased blood pressure or hypertension increases the risk of heart attack, cardiac arrest, brain stroke and other coronary artery diseases.
Obstructive sleep apnea also causes irregular heart rhythm known as arrhythmia. This may lower the blood pressure and may even cause death if the person already has underlying cardiovascular disorders.
Treatment and Diagnosis
Sleep apnea can be detected through a polysomnography test. This test monitors your overall activity during sleep, which includes- the activity of the vital organs- heart, lungs and brains, breathing pattern, and the oxygen level in your bloodstream.
If you are diagnosed with sleep apnea, your doctor might recommend positive airway pressure therapy. This therapy utilizes the Continuous Positive Airway Pressure (CPAP) machine. The CPAP is beneficial for people with this condition because it provides optimum air pressure through a mask-mechanism fitted over the mouth and nose. This reduces the chances of abnormal breathing trouble during sleep.
It is also advisable, you adjust your lifestyle and adapt to healthier habits. You may try to quit smoking, reduce alcohol consumption, exercise daily and try to lose weight.