What Is Obstructive Sleep Apnea?
Shallow breathing or pause of breathing briefly during sleep is a condition known as sleep apnea. Partial or complete blockage in the upper airway that makes breathing difficult during sleep occurs in those with Obstructive Sleep Apnea (OSA). Usually the person affected with sleep apnea is not aware of the condition he/she is suffering from.
Normal breathing vs. Sleep Apnea
Normal Breathing:
- While we sleep, we breathe in air by the contraction and downward movement of the diaphragm which increases the room in the chest cavity (the area into which the lungs expand).
- With the expansion of the lungs the air gushes in through the nose or mouth and travels down the windpipe into the lungs.
- This is where oxygen is absorbed by the air sacs.
- After the absorption of oxygen, the diaphragm expands by an upward movement in the chest cavity to resume its relaxed position.
- The CO2 rich air is the forced out of the nose or mouth due to this expansion of diaphragm.
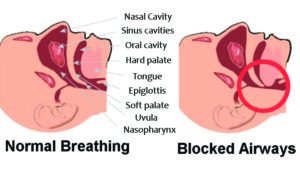
Obstructive Sleep Apnea:
For some individuals, the airway through the windpipe gets partially or completely blocked. Partial blockade leads to vigorous movement of the uvula which is audible as the snoring.
When the airway is completely obstructed airflow stops and the lungs is starved of air and oxygen. This event also wakes up the individual and the obstructed airway opens with a loud gasp or body jolt which is the body’s own method of pulling air back into the lungs. As one drifts off to sleep again the process is repeated and throughout the sleep the individual is repeatedly wakes up effectively leading to sleep deprivation.
No surprise the next day the person is tired and sleepy throughout the day!
Types of sleep apnea
Obstructive sleep apnea
- Most common
- Occurs because of blockage in the air passage by a soft tissue
- Causes loud snoring very often
Central sleep apnea
- Less common and involves the central nervous system
- Caused due to malfunctioning of muscles responsible for controlled breathing due to disruption in signal from the brain
- Affected ones usually do not snore.
According to a Philips Healthcare survey
- 58% of people think their work gets hampered due to disrupted sleep
- 11% falls asleep at workplace because of poor sleep at night
- 72% of Indians wake up more than once at night
- 33% of Indians snore during their sleep and believe it is normal to snore
- 14% people snore louder than they can speak
- Only 2% people talk about their snoring with their physician
Symptoms of OSA
- Dizziness during daytime or when at work
- Feeling thirsty after waking up in the morning
- Absent mindedness or not being able to concentrate
- Feeling choked while sleeping
- Waking up suddenly and often from sleep
- Snoring too loudly in sleep
- Difficulty in leaving bed in the morning
What are the risks of OSA?
- While people who are overweight or obese are at higher risks of getting sleep apnea, those who have a perfect BMI can get OSA too. 50% of those affected with OSA have been found to be overweight or obese. Weight reduction can play a role in lowering risks of getting OSA.
- Enlarged tonsils or adenoids can block the air passage and result in OSA.
- It is seen that the airways can be narrowed if someone suffers from chronic nasal congestion and their risk of getting OSA becomes twice than usual.
- Sudden drop in the level of oxygen flow can also cause heart diseases and may also cause cardiac arrest while asleep. Sudden deaths are much commoner with patients suffering from OSA.
- Asthma, like OSA, causes fragmented sleep as it poses difficulty in breathing. Those with asthma are more likely to get OSA.
- OSA patients usually suffer from high blood pressure and their control of blood pressure even with medication proves to be more tricky.
- Diabetes control also is more complicated for people suffering from OSA. CPAP therapy for OSA has been shown to ease Diabetes and hypertension control.
- Smoking is likely to increase risk of acquiring sleep apnea along with other major illnesses.
It is advisable not to ignore the symptoms of sleep apnea and delay treatment. Talk to your physician about OSA and know more about CPAP therapy.
What is CPAP Therapy?
CPAP stands for Continuous Positive Airway Pressure. It is a machine that ensures effective breathing by maintaining a continuous supply of airway pressure to the windpipe to keep it open and avoid sudden blockage that causes disrupted sleep.
https://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/obstructive-sleep-apnea/symptoms-causes/syc-20352090
https://www.helpguide.org/articles/sleep/sleep-apnea.htm
https://www.webmd.com/sleep-disorders/guide/understanding-obstructive-sleep-apnea-syndrome#1-1


Pingback:Obstructive Sleep Apnea - Expert Speak | Tribeca Care
Pingback:4 Realities of Life with Sleep Apnea | Tribeca Care